PHP web development remains one of the most reliable and widely used approaches to building modern websites and applications. Despite the rise of new technologies, PHP powers the majority of the web, from small business platforms to large-scale systems. For companies aiming to grow online, understanding how to structure projects for scalability, performance, and security is essential.
This practical guide to PHP web development will walk you through the key steps of creating applications that can handle increasing traffic and evolving business needs. By following best practices and proven strategies, you’ll be better prepared to build solutions that last and adapt.
Step 1 – Laying the foundations for PHP web development
Laying a strong foundation is crucial for successful PHP web development. By making informed choices regarding the PHP environment and frameworks, you can ensure a solid base for your application.
Choosing the right PHP version and environment
When starting a project, selecting the right PHP version is a crucial step. The version you choose directly impacts performance, compatibility, and long-term security.
According to W3Tech, PHP 8 powers 50% of PHP websites, while PHP 7 still accounts for 39.8%, and over 10% of sites run on outdated PHP 5.
- PHP 8.x – Delivers the best performance, modern features (like JIT compilation), and ongoing support.
- PHP 7.x – Still widely used but gradually reaching end-of-life; upgrading is strongly recommended.
- PHP 5.x and below – Unsupported, insecure, and should be avoided for any new project.
Partnering with an experienced PHP development company ensures you choose the right environment for scalability and long-term success.
Setting up frameworks, libraries, and dependencies for PHP web development
Choosing the right frameworks and libraries can significantly speed up development and reduce repetitive coding. They provide proven, reusable components that make PHP development services more efficient and maintainable. Among the most popular options are:
- Laravel – Known for its elegant syntax, built-in tools for authentication, and strong ecosystem for rapid application development.
- Symfony – Offers flexibility, scalability, and reusable components, making it a great fit for enterprise-level applications.
- CodeIgniter – Lightweight and easy to set up, perfect for smaller projects or when simplicity and speed are priorities.
Selecting the right framework ensures your project has a solid foundation tailored to its unique goals and complexity.
Step 2 – Designing scalable application architecture
Creating a scalable architecture is vital for accommodating future growth in your PHP web development projects. By employing robust structures, you can ensure that your applications maintain performance as they expand.
MVC and layered structures in PHP web development projects
In PHP web development, the Model–View–Controller (MVC) architecture is one of the most widely adopted patterns. It divides an application into three layers: the Model manages data and business logic, the View controls how information is displayed, and the Controller connects the two by handling user input and coordinating responses. This separation of concerns makes projects easier to manage, test, and scale over time.
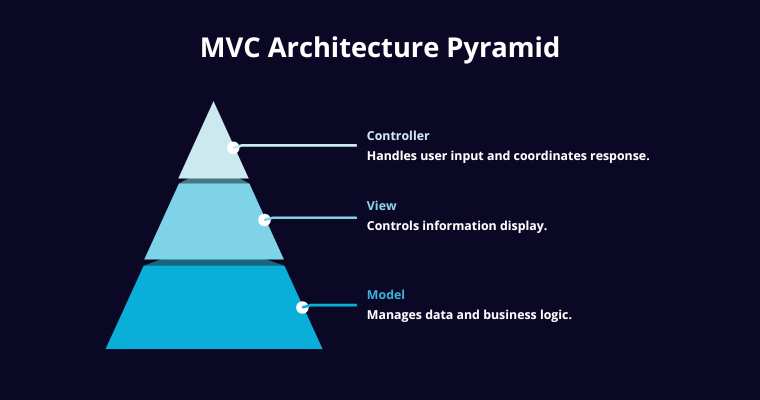
Beyond MVC, developers often apply layered structures, which introduce additional abstraction layers such as services, repositories, or APIs. These layers help decouple components even further, making large applications more modular and adaptable. When combined, MVC and layered structures provide a robust foundation for building scalable and maintainable PHP applications.
Database design and optimization strategies
Effective database design is foundational to the success of any application. A well-structured database not only ensures accurate data storage but also boosts performance and scalability in PHP development. Key strategies include:
- Normalization – Applying industry standards (such as First, Second, and Third Normal Form) to reduce redundancy, prevent anomalies, and maintain data integrity.
- Indexing – Creating indexes on frequently queried columns to accelerate data retrieval and improve response times.
- Query optimization – Writing efficient SQL queries, analyzing execution plans, and using caching to minimize server load.
By following these strategies, developers can design databases that remain reliable, consistent, and high-performing as applications grow in size and complexity.

Step 3 – Implementing best practices for scalability and security
Prioritizing scalability and security is paramount in PHP web development to protect your application from vulnerabilities. Following best practices can safeguard your application while ensuring it can handle increased loads as it grows.
Writing clean, modular, and testable PHP code
Clean, maintainable code is the backbone of successful PHP web development. By following principles such as clear naming conventions, consistent formatting, and meaningful comments, developers make their work easier to read and collaborate on. This clarity not only reduces errors but also speeds up onboarding when new team members join a project.
Equally important is writing modular and testable code. Breaking functionality into smaller, reusable components ensures that applications remain flexible and scalable as they evolve. Combined with practices like automated testing, this approach helps catch issues early and guarantees long-term stability.
Securing applications with authentication, validation, and encryption
Strong security practices are essential in PHP web development to protect both users and applications. Core areas to focus on include:
- Authentication – Implement methods such as multi-factor authentication, OAuth, or token-based systems to verify user identities and prevent unauthorized access.
- Validation – Apply strict input validation and sanitization to block malicious data, reducing the risk of SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other attacks.
- Encryption – Use proven encryption techniques to secure sensitive data both at rest and in transit, ensuring that intercepted information cannot be misused.
By addressing these three pillars, developers can build PHP applications that remain secure, trustworthy, and resilient against evolving threats.


Step 4 – Optimizing performance and ensuring maintainability
Performance optimization is key to providing users with a seamless experience in PHP web development. By focusing on maintainability, you can further future-proof your application, ensuring that it can evolve along with user needs.
Caching, load balancing, and server-side optimizations in PHP web development
Performance optimization is a cornerstone of PHP web development, helping applications remain fast, scalable, and reliable under heavy load. Key strategies include:
- Caching – Use mechanisms like file caching, Redis, or Memcached to store frequently accessed data and reduce database queries.
- Load balancing – Distribute traffic across multiple servers with tools like Nginx or HAProxy to prevent downtime and maintain consistent performance.
- Opcode caching – Enable PHP OPCache to store precompiled script bytecode in memory, reducing execution time for repeated requests.
- Database optimization – Improve query efficiency with indexing, connection pooling, and optimized schemas to minimize latency.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) – Offload static resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript to CDNs, reducing server strain and speeding up delivery.
- Server configuration tuning – Adjust PHP-FPM, memory limits, and thread handling to ensure efficient use of system resources.
By combining these strategies, developers can maximize performance and provide users with smooth, responsive experiences even as traffic scales.
Monitoring, debugging, and continuous integration
Monitoring is essential in PHP web development, as it provides real-time insights into application health, server performance, and error rates. With proper monitoring tools in place, developers can quickly identify bottlenecks and address issues before they affect users. Debugging plays a complementary role by allowing teams to trace problems back to their root cause, whether through detailed error logs, breakpoints, or profiling tools. This ensures faster resolutions and minimizes downtime.
Continuous integration (CI) further enhances the development process by automating testing and deployment workflows. Each code change is validated against a set of predefined tests, reducing the risk of introducing bugs into production. CI pipelines also allow teams to deliver updates more frequently and with greater confidence, supporting agile development practices. By combining monitoring, debugging, and CI, PHP projects become more stable, scalable, and adaptable to changing business needs.

FAQ - PHP web development
Why is PHP still a good choice for web development in 2025?
PHP continues to be a reliable option thanks to its maturity and adaptability in modern projects.
- It powers the majority of websites worldwide, with strong community support and extensive documentation.
- Frameworks like Laravel and Symfony keep it relevant by introducing modern features and best practices.
- Ongoing updates to PHP ensure compatibility with cloud-native solutions and integration with emerging technologies.
Together, these factors make PHP a future-proof choice for building scalable and secure applications.
How can PHP support legacy app modernization?
PHP is well suited for legacy app modernization because it allows teams to rebuild or extend existing systems step by step rather than rewriting everything from scratch. By creating modern PHP-based modules, APIs, or microservices around an older core, businesses can gradually replace outdated components while keeping critical operations online. This approach reduces risk, shortens downtime, and makes it easier to introduce new features, security improvements, and performance optimizations over time.
What are the best PHP web development frameworks for building scalable applications?
Popular PHP frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter offer excellent tools for building scalable applications. They provide built-in features that simplify common tasks, helping a PHP development company deliver efficient solutions that can grow with your needs.
How to ensure your PHP web development future-proof?
Future-proofing a PHP application requires planning for long-term stability and adaptability. The most effective ways to achieve this include:
- Writing clean, modular code that can be easily tested, maintained, and extended.
- Using established frameworks like Laravel or Symfony that evolve alongside industry best practices.
- Following recognized coding standards (such as PSR guidelines) to ensure consistency across teams and projects.
- Keeping dependencies, libraries, and PHP versions updated to benefit from security patches and performance improvements.
By combining these practices with continuous learning, your application will remain reliable and relevant in the years ahead.
Is PHP a good choice for ERP modernization projects?
Yes, PHP is a strong option for ERP modernization because it supports building modular, API-driven architectures that integrate with existing databases and services. Using frameworks such as Laravel or Symfony, development teams can refactor legacy ERP modules, expose core functions through secure APIs, and gradually move toward more flexible web-based interfaces. This helps organizations modernize their ERP systems without disrupting day-to-day operations, while improving performance, usability, and maintainability.
Do I need a software house to build a scalable PHP application?
While it's possible to develop a scalable PHP application on your own, partnering with a specialized software house can streamline the process. Their expertise in PHP web development ensures best practices are followed, leading to more robust, secure, and maintainable applications.